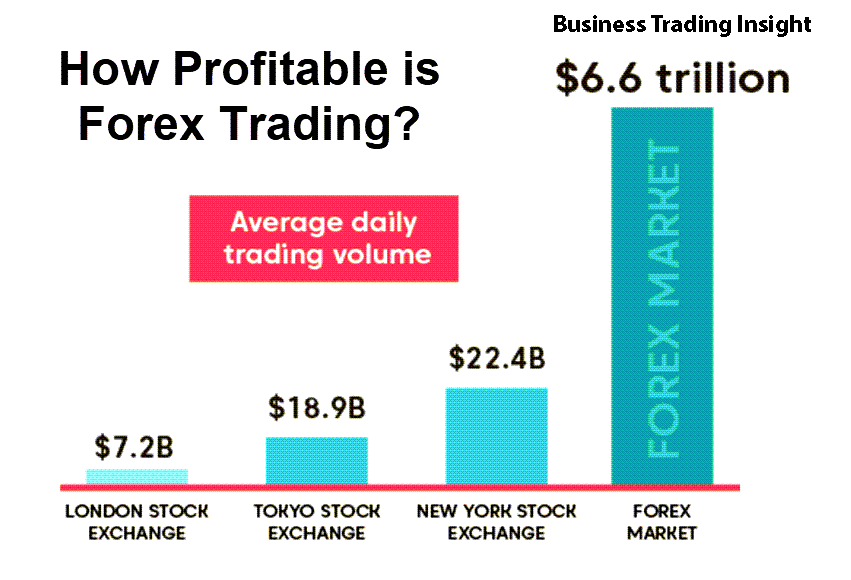
The Forex broker is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with daily trading volumes exceeding $6 trillion. Its vast scale and 24/7 accessibility make it a critical component of the global financial system. Traders in this market engage in the buying and selling of currency pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, and USD/CHF, aiming to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. However, retail traders cannot directly access the Forex market without the assistance of a Forex (foreign exchange) market.
So, what is a broker in forex, and what role do they play in this high-stakes market? In this article, we will delve into the fundamental responsibilities of a Forex broker, how they function in the trading environment, the services they provide, and how you can choose the right broker for your trading needs.
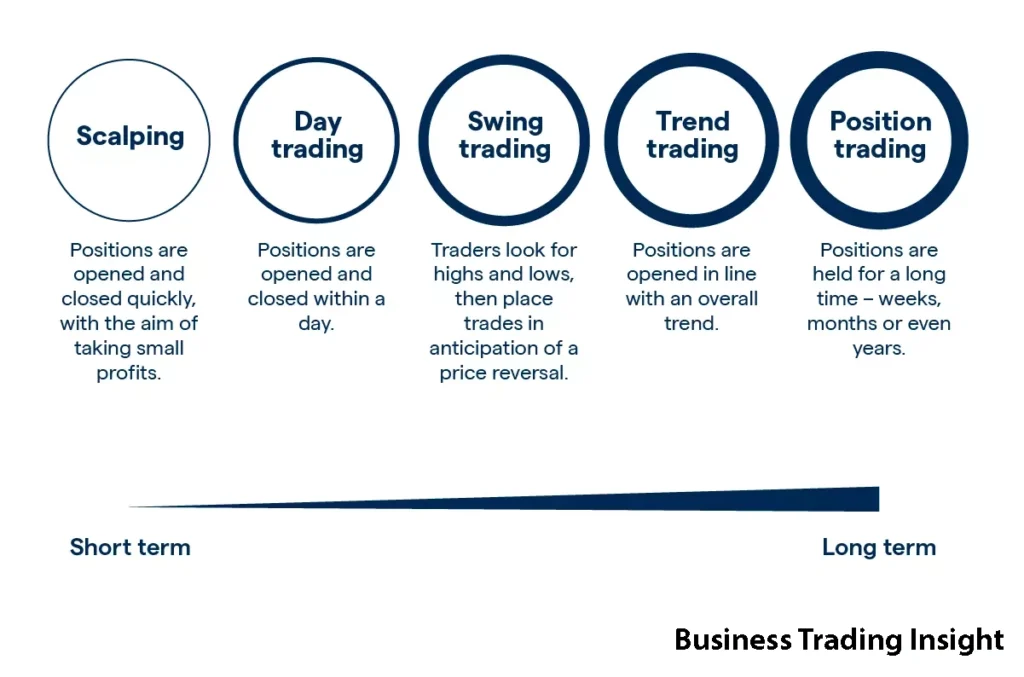
Overview of Forex Trading
Before exploring the specifics of the broker’s role in Forex trading, it’s essential to understand the basic structure of the Forex market. The Forex market operates through a decentralized network of global banks, financial institutions, and brokers. Unlike other financial markets, there is no single exchange where all Forex transactions occur. Instead, Forex trading is conducted via a network of participants spread across multiple locations and time zones.
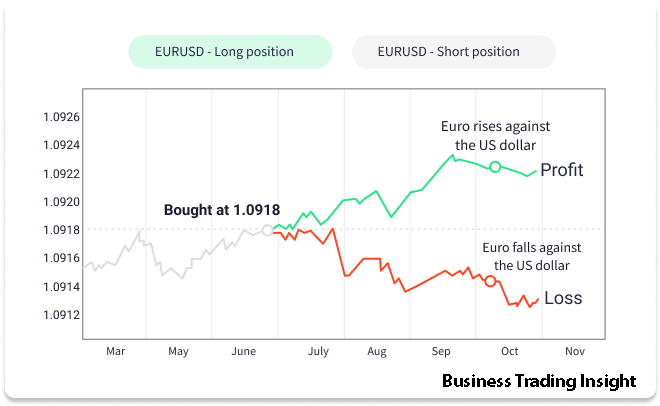
At its core, Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another, in pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, or GBP/USD. Traders speculate on whether the price of a currency will rise or fall relative to another, aiming to profit from these movements. The Forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, making it highly accessible to traders worldwide.
In this vast market, brokers play a critical role as intermediaries that connect retail traders to the liquidity providers (e.g., banks, hedge funds, and large financial institutions) who actually execute the trades. Understanding the role of a broker in forex trading is key to navigating this dynamic and potentially profitable market.
What is a Forex Broker?
Definition
What is a broker in Forex? A Forex broker is a financial service provider that facilitates currency trading by offering retail traders access to the Forex market. They act as intermediaries between traders and liquidity providers (such as banks, financial institutions, and market makers) who are responsible for executing the actual trades. Forex brokers provide platforms for traders to place buy or sell orders on currency pairs, offering various services that help traders execute their strategies effectively.
The primary function of a Forex broker is to provide market access and trade execution. Brokers allow traders to speculate on currency price movements by offering trading platforms that connect them to liquidity pools, where they can buy and sell currencies. By understanding what is a broker in Forex, traders can better appreciate the broker’s role in facilitating their access to the global currency market.
The Broker’s Function
The core responsibility of a Forex broker is to provide a bridge between the retail trader and the interbank market. The interbank market is a network where large financial institutions trade currencies directly with one another. Forex brokers facilitate this access by acting as a middleman, linking traders to liquidity providers. They aggregate liquidity from these institutions and present it to their clients, typically offering real-time pricing and the ability to place orders in the market.
Brokers provide more than just access—they also provide leverage, which allows traders to control larger positions with less capital. For example, if a broker offers 100:1 leverage, a trader can control $100,000 in currency with only $1,000 of their own capital. This leverage can magnify potential profits but also increases the risk of substantial losses. Understanding what is a broker in Forex can help traders make better decisions regarding leverage, as it plays a significant role in both potential profits and risks.
In short, the broker’s function is to connect the trader to the liquidity providers, offer a platform for trade execution, and provide essential tools that help traders make informed decisions. Knowing what is a broker in Forex allows traders to understand the importance of choosing the right intermediary to support their trading goals and strategies.

Types of Forex Brokers
Not all Forex brokers operate the same way. What is a broker in Forex? A Forex broker is an intermediary that provides retail traders with access to the global currency market. However, brokers can differ significantly in how they operate, their fee structures, and the type of services they provide. There are different types of brokers, each offering distinct trading conditions, fee structures, and access to liquidity. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right broker based on your trading style.
Market Makers
Market makers are brokers that create their own buy and sell prices for currency pairs and act as the counterparty to their clients’ trades. This means that when a trader buys a currency pair, the market maker is selling it to them, and vice versa. Market makers are often associated with fixed spreads, meaning that the difference between the buying and selling price remains constant regardless of market conditions.
The major advantage of market makers is that they provide liquidity, especially in volatile markets, which means that trades can be executed quickly even in less liquid pairs. However, a potential downside is the conflict of interest. Since market makers are the counterparty to traders’ positions, they might benefit when a trader loses, creating a potential for unfair execution practices. Understanding what is a broker in Forex helps traders recognize the potential advantages and risks of this type of model.
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) Brokers
ECN brokers provide access to a network where traders can place orders that are directly matched with other buyers or sellers in the market. Unlike market makers, ECN brokers do not act as the counterparty to a trade. Instead, they simply match orders within the liquidity pool, offering better pricing transparency and tighter spreads. This type of broker is popular with professional traders who want direct market access and to avoid potential conflicts of interest.
ECN brokers generally charge a commission per trade, rather than making money through markups on the spread. This can make trading with an ECN broker more cost-effective for frequent traders. The disadvantage is that, unlike market makers, the bid/ask spread can vary depending on market liquidity, which can sometimes make it less predictable for new traders. By understanding what is a broker in Forex, traders can evaluate whether ECN brokers’ transparent pricing structure aligns with their trading needs.
STP (Straight Through Processing) Brokers
STP brokers route clients’ orders directly to liquidity providers, bypassing any manual intervention. This system ensures that trades are executed quickly and efficiently, without the broker acting as the counterparty. STP brokers often offer variable spreads and sometimes charge a commission on each trade.
STP brokers are often preferred by traders who value transparency and want to avoid conflicts of interest. The key benefit of STP brokers is that they offer faster execution and lower spreads compared to market makers, making them ideal for traders who need efficient, high-frequency trade execution. Understanding what is a broker in Forex helps you understand the value of STP brokers in providing seamless access to the market.
DMA (Direct Market Access) Brokers
DMA brokers offer the highest level of access to the markets, providing traders with direct access to liquidity pools and exchanges. DMA brokers allow traders to place orders directly in the market, bypassing any intermediary steps. This gives traders more control over trade execution and results in lower slippage.
DMA brokers are typically used by high-frequency traders, institutional traders, and algorithmic traders who require minimal interference and the ability to place large orders in the market. Understanding what is a broker in Forex and the benefits of direct market access is essential for those looking to engage in high-frequency or algorithmic trading.
How Forex Brokers Make Money
Forex brokers are in business to make money, and they do so in various ways. But what is a broker in Forex? In simple terms, a Forex broker is a financial intermediary that connects retail traders to the larger, institutional Forex market. They facilitate the execution of trades and provide the necessary tools for trading currencies. Here are some of the common revenue models:
Spreads
The spread is the difference between the bid (selling) price and the ask (buying) price of a currency pair. Forex brokers typically make money by charging a spread on each trade. A broker may charge either a fixed spread or a variable spread depending on the type of broker.
In fixed spreads, the bid and ask prices remain constant, regardless of market conditions, while variable spreads fluctuate based on market demand and liquidity. Brokers with fixed spreads may offer more predictable pricing, but brokers with variable spreads can provide tighter spreads during times of high liquidity.
Commissions
Some brokers, particularly ECN and STP brokers, charge a commission on each trade in addition to the spread. This commission is usually a fixed amount based on the volume of the trade. ECN brokers, for example, offer lower spreads but charge a commission for the trade execution, whereas STP brokers may offer tighter spreads without charging a commission.
Swap or Rollover Fees
When traders hold positions overnight, they may be charged or credited with swap fees or rollover fees. These fees depend on the interest rate differential between the two currencies being traded. Forex brokers typically pass on these charges to traders who maintain positions overnight.
For example, if a trader is long on a currency pair where the base currency has a higher interest rate than the quote currency, they may earn a rollover credit. On the other hand, if the base currency has a lower interest rate, the trader may incur a rollover fee.
Markups on Spreads
Market-making brokers often increase the spread they offer to traders, adding a markup to the difference between the bid and ask price. This allows market makers to profit directly from the trades executed through their platform. While the spread is generally more predictable, it can sometimes be higher than in ECN or STP accounts, making market-making brokers less favorable for traders who want the best possible execution prices.
By understanding what is a broker in Forex and how they earn money through spreads, commissions, and other fees, traders can make more informed decisions when choosing a broker that fits their trading strategy and financial goals.
Key Features to Look for in a Forex Broker
When selecting a Forex broker, it’s important to first understand what is a broker in Forex. A Forex broker acts as the intermediary between retail traders and the global currency market, providing access to trading platforms, liquidity, and other necessary services. By selecting the right broker, traders ensure they can execute their trades effectively while aligning with their trading style, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
Regulation
The most critical factor in choosing a broker is ensuring that they are regulated by a reputable authority. A regulated broker is bound by strict financial laws and regulations that protect traders. Some of the major regulatory bodies include:
- FCA (Financial Conduct Authority) in the UK
- NFA (National Futures Association) in the US
- ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission) in Australia
- CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission) in Cyprus
These regulatory bodies ensure that brokers follow fair trading practices, maintain segregated accounts for client funds, and provide adequate investor protection schemes. Understanding what is a broker in Forex and their regulatory framework is crucial for ensuring the safety of your funds.
Trading Platforms
The trading platform is the most crucial tool a trader will use, so choosing a broker that offers a reliable and user-friendly platform is essential. Some of the most popular platforms include:
- MetaTrader 4/5 (MT4/MT5): A widely used platform with advanced charting tools, technical analysis capabilities, and the ability to automate trades via Expert Advisors (EAs).
- cTrader: Known for its intuitive interface and advanced charting features.
- Proprietary Platforms: Some brokers offer their own custom-built platforms, which can include unique features like social trading, integrated research, or improved mobile interfaces.
The platform you choose can significantly impact your trading experience, making it important to consider which broker offers the tools and features that align with your trading style.
Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, which can magnify both profits and losses. Brokers typically offer leverage ratios, such as 50:1, 100:1, or 500:1. While leverage can enhance trading opportunities, it can also increase the risk of significant losses if not used responsibly. What is a broker in Forex in this context? They provide the leverage that allows you to maximize your exposure to the market, but they also ensure that you are aware of the risks involved.
Customer Support
Effective customer support is essential for ensuring that any issues or questions are quickly addressed. Traders should look for brokers who offer 24/7 support via multiple channels, including phone, email, and live chat. Additionally, brokers who provide multilingual support are a plus for traders from different regions. Understanding what is a broker in Forex also involves knowing that their customer service can be just as important as the platform they provide for executing trades.
Deposit and Withdrawal Methods
A reliable Forex broker should offer multiple methods for depositing funds and withdrawing profits. These methods include bank transfers, credit/debit cards, and e-wallets such as PayPal, Skrill, or Neteller. Traders should check for any hidden fees and the speed at which withdrawals are processed. When selecting a broker, make sure that the payment methods align with your preferences, as well as understanding how easy it is to transfer funds to and from your account.
Account Types
Brokers offer various account types designed for different trader profiles. Some common account types include standard, micro, mini, and ECN accounts. Each account type comes with different minimum deposit requirements, spreads, and leverage options. It’s important to understand the nuances of what is a broker in Forex and the types of accounts they offer, as this will allow you to select the one that best fits your trading needs and goals.inimum deposit requirements, spreads, leverage ratios, and available features. Traders should select the account type that best fits their trading style, risk tolerance, and capital size.
Conclusion
Summary of Broker’s Role
The Forex broker serves as the gateway between retail traders and the global currency market. But what is a broker in Forex? In simple terms, a Forex broker is an intermediary that connects individual traders with the liquidity providers, such as banks and financial institutions, allowing them to buy and sell currencies. They facilitate market access, provide trading platforms, and offer various tools and resources to assist traders in executing their strategies. Understanding the role of the broker in the Forex market is essential for anyone looking to trade currencies successfully. Without a reliable broker, accessing the global Forex market would be nearly impossible for retail traders.
Choosing a Broker Wisely
Choosing the right Forex broker is a critical decision that can significantly impact your trading success. When you understand what is a broker in Forex, you realize that their role is not just about providing access to the market. You also need to consider other factors such as regulation, trading platforms, fees, leverage, and customer support when making your selection. Always ensure that the broker is regulated by a reputable authority to ensure that your funds are protected and that the broker follows strict industry standards for fair play.
Final Thoughts on Risk Management
While brokers provide the tools and access necessary for Forex trading, risk management ultimately lies in the hands of the trader. By understanding what is a broker in Forex, you also understand the importance of utilizing appropriate leverage, setting stop-loss orders, and maintaining discipline in your trading approach. Brokers offer essential resources and platforms, but it’s the trader who must navigate the complexities of the market. By selecting a reputable broker and following sound trading practices, traders can increase their chances of success in the complex and dynamic Forex market.
FAQ
How do Forex brokers make money?
Forex brokers generate revenue in several ways: through spreads (the difference between buying and selling prices), commissions on trades, swap or rollover fees for positions held overnight, and markups on spreads, especially in market-making brokers.
What types of Forex brokers are there?
There are four main types of Forex brokers:
- Market Makers: They set their own buy and sell prices and act as the counterparty to trades.
- ECN Brokers: Provide direct market access, matching traders' orders with others in the market, offering tighter spreads and more transparency.
- STP Brokers: Route client orders directly to liquidity providers, offering faster execution and lower spreads.
- DMA Brokers: Offer direct access to the market, bypassing intermediaries for minimal interference, typically used by high-frequency traders.
What is leverage, and how does it work in Forex trading?
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. For example, with 100:1 leverage, a trader can control $100,000 with just $1,000. While leverage amplifies potential profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
What is the difference between fixed and variable spreads?
A fixed spread remains constant regardless of market conditions, providing predictability in pricing, while a variable spread fluctuates based on market liquidity and conditions, often offering tighter spreads during times of high liquidity.



