The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume that exceeds $6 trillion. Central to understanding price movements in this market is the concept of supply and demand forex. These fundamental economic principles, which govern how prices are determined in any market, are especially crucial in the forex market where currencies are traded in pairs.
In the forex market, currency pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD, are the vehicles through which traders exchange one currency for another. The value of a currency pair is determined by the relative supply and demand for each of the currencies in the pair. A surge in demand for a particular currency pushes its price up, while an oversupply of that currency leads to a decrease in its value. Understanding supply and demand forex dynamics allows traders to identify potential market opportunities, predict price movements, and optimize their trading strategies.
This article will dive deep into how supply and demand forex influences price movements, the factors that impact the supply and demand of currencies, and how traders can implement this knowledge in their strategies. By the end of this article, you’ll understand how supply and demand forex drive price changes and how to use this to improve your trading.
What is Supply and Demand in Forex?
Basic Economic Definition
In its most basic form, supply refers to the quantity of a good or asset that sellers are willing to offer at various price points, while demand refers to the quantity that buyers are willing to purchase at these same price points. In traditional markets, when demand exceeds supply, prices rise; when supply exceeds demand, prices fall. This balance — or imbalance — between buyers and sellers forms the foundation of price movements.
In the context of forex trading, this principle is applied in the same way, but with one important difference: currencies are traded in pairs. Supply and demand forex determines the value of one currency relative to another, which is reflected in the exchange rate of a currency pair. This interaction is key to understanding how currency prices move and why forex traders must monitor supply and demand closely.
Supply and Demand in the Forex Market
In forex trading, currencies are traded in pairs. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro is the base currency, and the US dollar is the quote currency. The exchange rate between these two currencies reflects how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. The interplay of supply and demand forex between the two currencies determines the direction in which the pair moves.
When demand for the base currency increases, its value rises relative to the quote currency. For example, if investors believe that the European economy is performing well, the demand for the euro will increase, and the EUR/USD pair will rise. Conversely, if there is an oversupply of the base currency, the exchange rate will fall.
The concept of supply and demand forex is especially important because the forex market is not influenced by a single seller or buyer. Instead, it is shaped by the collective actions of central banks, institutional investors, hedge funds, and retail traders, all reacting to economic indicators, geopolitical events, and other market forces.
Currency Pairs and Supply-Demand Dynamics
When trading forex, each currency pair consists of two currencies, and the exchange rate reflects the balance of supply and demand forex for each currency. For example, if the demand for the US dollar increases relative to the euro, the value of the USD rises, which drives the EUR/USD exchange rate down.
Because forex trading operates in pairs, traders need to pay attention to both currencies in the pair. Even if one currency experiences a strong demand increase, the other currency in the pair must also be considered, as it may be experiencing an opposite force (either a decline in demand or an increase in supply). This is where understanding supply and demand forex becomes complex, as it’s not just about the currency you’re buying but also about how the counterpart is behaving in the market.
The Impact of Supply and Demand on Forex Price Movements
Price Determination
At its core, the price of a currency pair in forex is determined by the forces of supply and demand forex. When demand for a currency increases (for example, when investors expect the currency’s value to rise), the price of that currency rises. Conversely, when demand weakens, or when supply of the currency increases, its price will fall.
In the forex market, price determination is a continuous process driven by the ever-changing balance of supply and demand. Central banks, investors, and traders all influence this dynamic, leading to constant fluctuations in exchange rates.
For example, when a central bank like the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, this tends to increase the demand for the US dollar, as investors are attracted by the higher return on investments denominated in USD. As a result, the supply and demand forex forces push the value of the dollar higher, which causes the EUR/USD exchange rate to decline.
Price Action and Market Balance
Price action refers to the price movements of a currency pair over time. These movements reflect the ongoing balance — or imbalance — between supply and demand forex. When demand exceeds supply, the price rises, and when supply exceeds demand, the price falls. This constant adjustment leads to price fluctuations, creating the market conditions that traders try to capitalize on.
Understanding price action is key to identifying areas of support and resistance. Support refers to a price level at which demand is strong enough to prevent the price from falling further, while resistance is a level where supply is strong enough to prevent the price from rising. By analyzing price action and understanding supply and demand forex, traders can predict potential reversals or trend continuations.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Trends
Supply and demand forex can lead to both short-term fluctuations and long-term trends. In the short term, news events, economic data releases, and changes in investor sentiment can quickly shift the balance between supply and demand, causing significant price movements. On the other hand, in the long term, broader economic factors such as interest rates, GDP growth, and inflation typically drive the supply and demand dynamics of a currency.
For traders, understanding both the short-term and long-term effects of supply and demand forex is essential for developing effective trading strategies. Short-term traders may focus on reacting to news and price action, while long-term traders may base their decisions on fundamental factors that affect currency supply and demand.
Factors Influencing Supply and Demand in Forex
Macroeconomic Indicators
Several key macroeconomic indicators influence supply and demand forex:
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by central banks play a pivotal role in determining currency demand. Higher interest rates tend to increase demand for a currency because they offer higher returns on investments. Conversely, lower interest rates reduce demand, as investors look for higher-yielding opportunities elsewhere.
When a central bank like the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it often leads to an increase in demand for the US dollar, resulting in a higher USD value. Conversely, if interest rates are cut, the currency may weaken as investors seek better returns elsewhere.
GDP and Economic Health
The overall economic health of a country directly impacts the supply and demand forex for its currency. A country with strong economic growth typically sees increased demand for its currency, as investors flock to capitalize on the nation’s growth potential. Conversely, a country with weak economic performance may see reduced demand for its currency.
Inflation
Inflation is another important factor that affects currency supply and demand. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, making it less attractive to investors. In contrast, low inflation supports a currency’s value, as it indicates stable economic conditions and a predictable economic environment.
Geopolitical Events
Political Stability
Political events, such as elections, government policies, or geopolitical tensions, can dramatically influence the supply and demand forex for a currency. Political stability typically boosts investor confidence in a currency, increasing demand. In contrast, political instability (such as wars or government instability) can lead to reduced demand, as investors may seek safer assets.
For example, the Brexit referendum in 2016 caused significant shifts in the supply and demand forex dynamics of the British pound, as uncertainty about the UK’s future within the European Union led to a decline in the pound’s value.
Global Crises
Global crises, such as financial crashes, pandemics, or natural disasters, can create significant shifts in supply and demand forex. During times of crisis, traders often flock to safe-haven currencies like the US dollar or the Swiss franc, increasing demand for these currencies and causing their value to rise.
For instance, during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for the US dollar spiked as investors sought the safety and liquidity of the world’s most widely traded currency.
Market Sentiment and Speculation
Investor Perception
Investor sentiment — shaped by news, rumors, and broader economic developments—can cause sharp shifts in supply and demand forex. If investors perceive a currency as likely to strengthen due to a positive economic report or news event, demand for that currency will increase, pushing the price higher.
Speculation and Risk Appetite
Investor behavior, influenced by risk appetite, also affects currency supply and demand. When markets are risk-on, investors may be more willing to invest in higher-yielding, riskier currencies. Conversely, in risk-off periods, investors tend to seek out safer assets, driving up demand for stable currencies like the USD or the JPY.
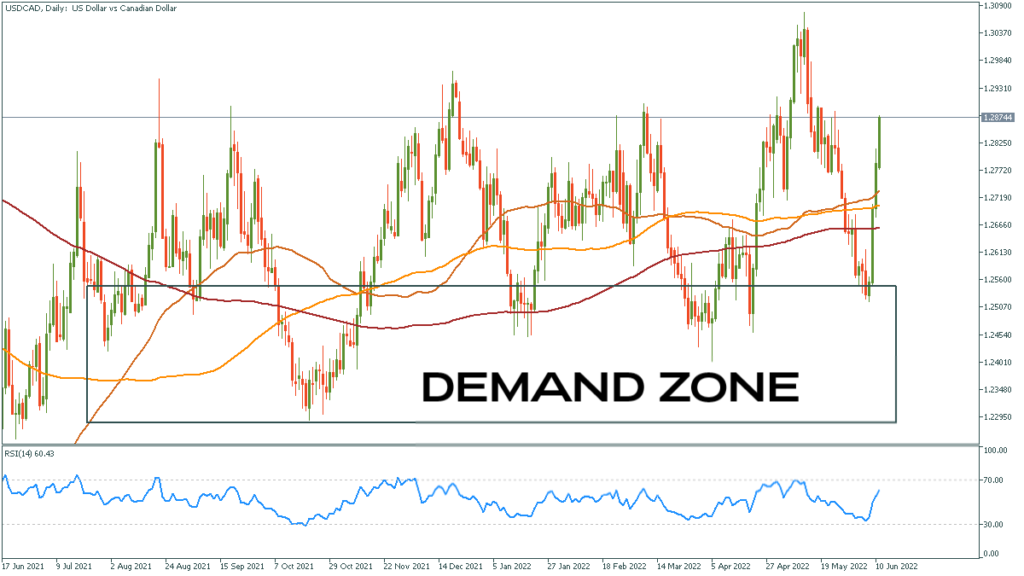
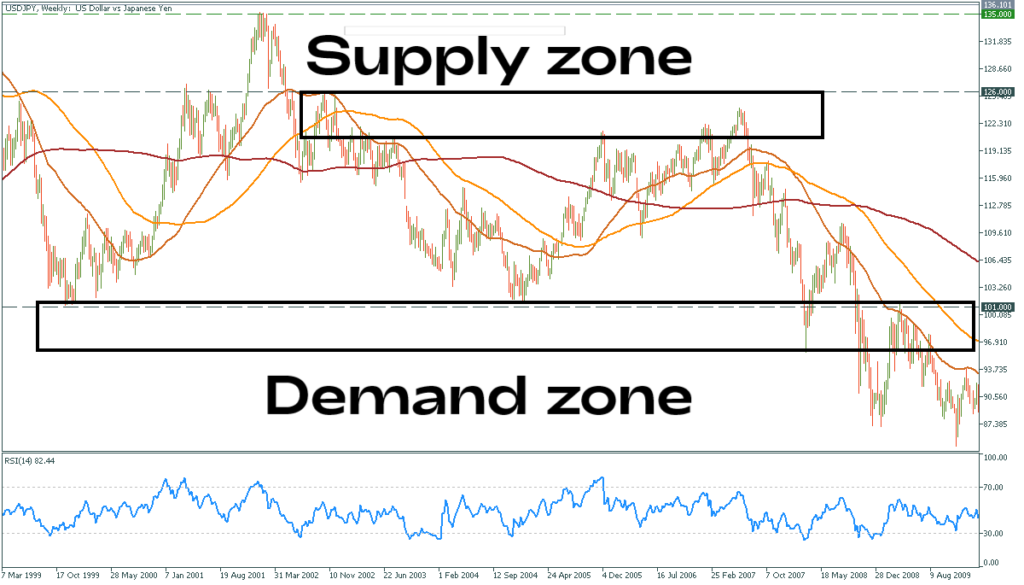
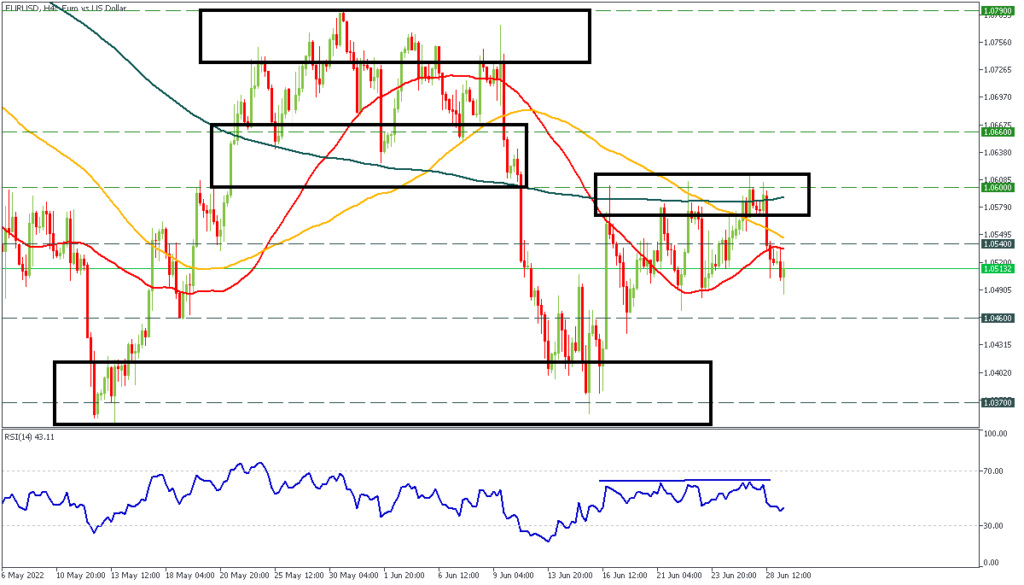
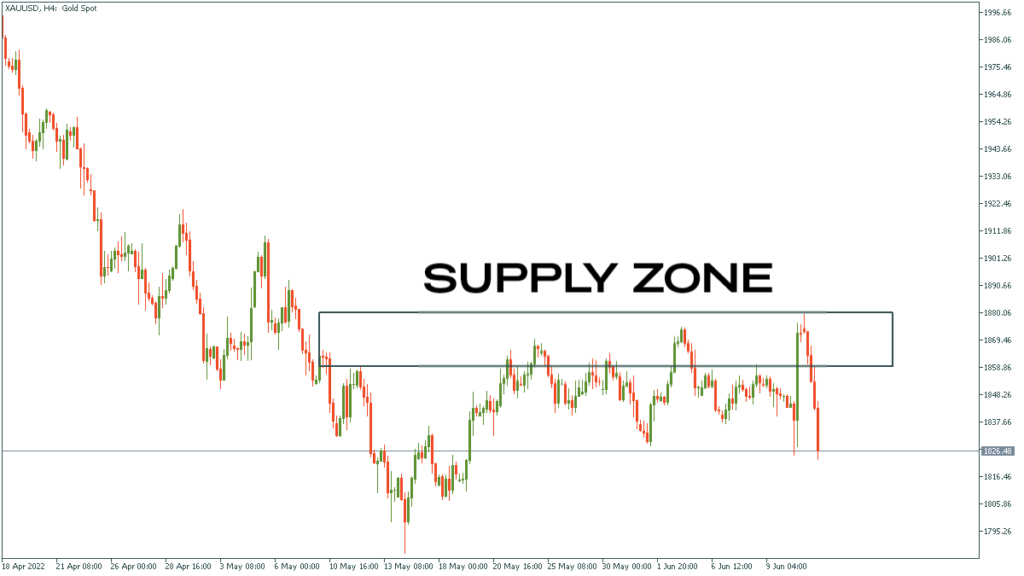
Supply and Demand Zones in Forex Trading
What Are Supply and Demand Zones?
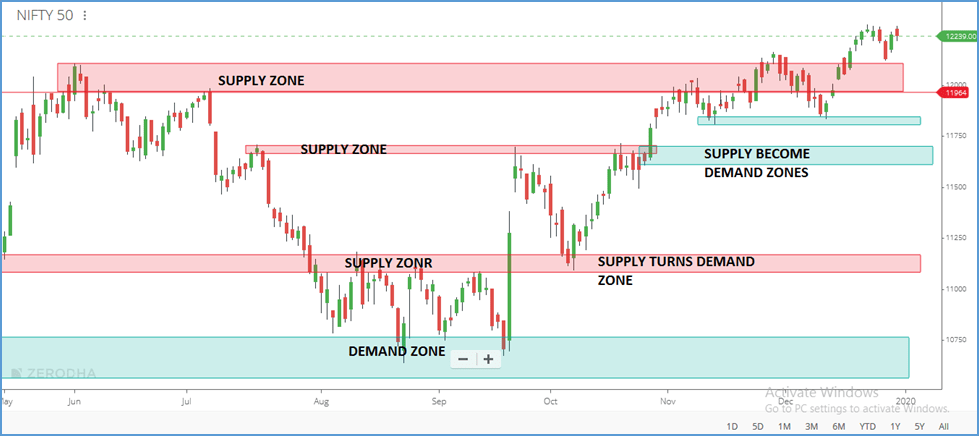
Supply and demand zones are key price areas on a chart where there has historically been either a concentration of buying (demand) or selling (supply). These zones are important because they represent areas where price has previously reversed, making them ideal areas for traders to look for future price movements.
Identifying Supply and Demand Zones
Traders use historical price data, volume analysis, and price action forex to identify supply and demand zones. Strong supply and demand zones often align with significant price levels, such as support and resistance, where price has bounced or reversed multiple times in the past.
Reversal Zones
When price approaches a supply or demand zone, it often experiences a reversal. Traders use this behavior to anticipate future price movements. A strong demand zone, where price tends to rise, may present a buying opportunity, while a supply zone, where price tends to fall, may present a selling opportunity.
Order Flow and Imbalances
Order flow refers to the buying and selling activity in the market. Large institutional orders, for example, can create significant supply and demand forex imbalances, which in turn drive sharp price movements. Recognizing these imbalances allows traders to predict price shifts before they occur.
Supply and Demand as Leading Indicators
Experienced traders use supply and demand forex zones as leading indicators, as they can provide clues about where price is likely to move next. By analyzing price action around these zones, traders can predict potential reversals or trend continuations and enter trades with high probability setups.
Conclusion
In summary, supply and demand forex is the fundamental force driving price movements in the currency market. By understanding how these forces work — how central banks, economic indicators, and geopolitical events shape the demand and supply of currencies — traders can identify key entry and exit points for successful trades. Recognizing supply and demand zones and using them to inform trading decisions can significantly improve a trader’s ability to anticipate price movements and manage risk.
As a forex trader, it’s essential to integrate supply and demand forex analysis with broader market conditions and economic fundamentals. By doing so, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the complex dynamics of the forex market and develop a trading strategy that maximizes your success.