In the world of trading, recognizing patterns and market behavior is crucial for making informed decisions. Among these behaviors, pullbacks hold significant importance. Understanding pullbacks can help traders navigate market trends effectively, making them a key concept in technical analysis.
What Is a Pullback?
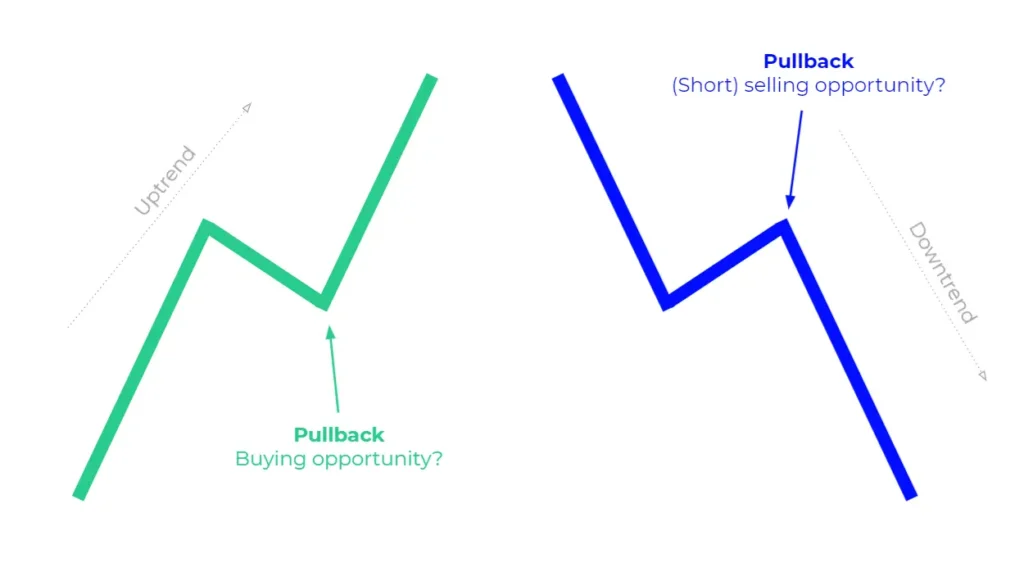
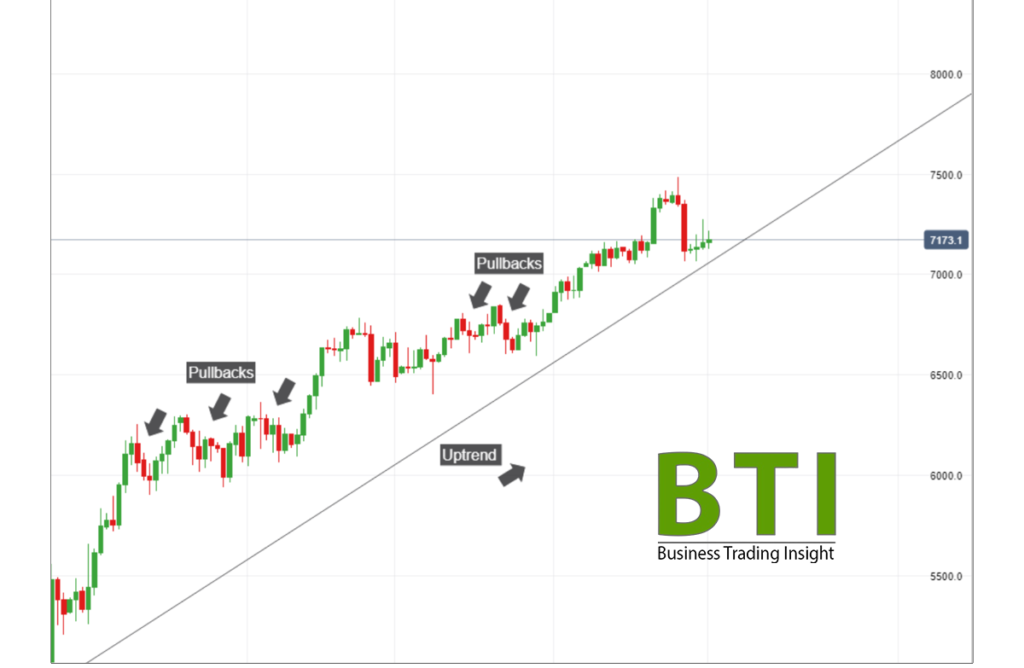
A pullback in trading is a temporary price retracement in a financial asset within a prevailing trend. Specifically, it refers to a situation where the price moves against the dominant trend, creating a brief decline in an uptrend or a rise in a downtrend. This phenomenon is often seen as a natural part of market movements, providing traders with potential entry points.
Characteristics of Pullbacks
Key features of pullbacks include:
- Temporary Nature: Pullbacks are typically short-lived and often occur before the original trend resumes.
- Trend Alignment: They occur within the context of a broader trend—either upward or downward.
- Volume Changes: During a pullback, trading volume may vary; a decrease in volume can indicate a lack of conviction among sellers or buyers.
Market Context
Pullbacks are common in various market scenarios:
- Uptrends: In an uptrend, pullbacks allow for potential buying opportunities as the price retraces before continuing to rise.
- Downtrends: Conversely, in a downtrend, pullbacks can present selling opportunities as prices briefly rise before resuming their decline.
What Does a Pullback Tell You?

Market Sentiment
Pullbacks can provide insights into investor sentiment. A pullback during an uptrend may signal profit-taking among traders but can also indicate that the trend remains intact if buyers re-enter the market. Conversely, in a downtrend, a pullback might suggest hesitation among sellers, providing clues about potential trend reversals.
Buying and Selling Opportunities
For traders, pullbacks create crucial opportunities:
- Entry Points: Traders often use pullbacks to enter positions at a more favorable price, anticipating the continuation of the trend.
- Exit Points: Existing traders may utilize pullbacks to determine optimal exit points, locking in profits before a potential reversal.
Confirmation of Trend Strength
The behavior of prices during a pullback can indicate the strength of a trend:
- Strong Trend: If the price quickly rebounds after a pullback, it suggests strong underlying momentum.
- Weak Trend: Conversely, if the price struggles to recover, it may indicate weakening trend strength and potential reversal.
Example of How to Use a Pullback
Step-by-Step Guide
Traders can follow these steps to identify and utilize pullbacks in their strategies:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify the Trend | Use moving averages or trend lines to determine the prevailing market direction. |
| Wait for a Pullback | Monitor for a retracement against the trend, ideally accompanied by decreasing volume. |
| Confirm Reversal | Look for signs that the pullback is concluding, such as bullish candlestick patterns in an uptrend or bearish patterns in a downtrend. |
| Enter the Trade | Execute the trade once confirmation signals align with the trend. |
Case Study
Consider a stock that has been in a strong uptrend, moving from $50 to $70. After reaching $70, it retraces to $65. Traders observing this pullback might look for confirmation through candlestick patterns or volume spikes at $65, indicating a possible re-entry point before the price continues upward.
Entry and Exit Strategies
When trading pullbacks, effective strategies include:
- Entry: Place buy orders slightly above the high of the pullback.
- Exit: Set a profit target based on the distance of the previous price move before the pullback, or use trailing stops to maximize gains.
The Difference Between a Reversal and a Pullback
Definition of Reversal
A market reversal is a significant change in the direction of price movement, indicating a shift from an uptrend to a downtrend or vice versa. Unlike a pullback, which is temporary, a reversal suggests a more lasting change in market sentiment.
Key Differences
To differentiate between pullbacks and reversals, consider the following:
- Duration: Pullbacks are short-lived; reversals tend to last longer.
- Price Behavior: A pullback often retraces a portion of the previous move, while a reversal typically changes the trend’s direction.
- Volume Patterns: Volume may decrease during a pullback, while a reversal often shows increasing volume as new sentiment emerges.
Identifying Each
Traders can use specific indicators to distinguish between a pullback and a potential reversal:
- Moving Averages: Crossovers can signal a reversal, whereas pullbacks often stay above or below certain moving averages.
- Momentum Indicators: Oscillators like RSI can indicate overbought or oversold conditions, providing clues on whether a price move is a pullback or a reversal.
Limitations in Trading Pullbacks
False Signals
One major risk in pullback trading is the occurrence of false signals. Not every price retracement is a genuine pullback; sometimes, these can lead to further declines or reversals, causing losses for traders who enter positions too early.
Market Conditions
Market conditions play a significant role in the reliability of pullbacks. For example:
- High Volatility: In volatile markets, pullbacks may be exaggerated, leading to unpredictable price movements.
- News Events: Economic announcements or geopolitical events can drastically alter market conditions, affecting pullbacks and their validity.
Emotional Trading
Traders may struggle with emotional decision-making during pullbacks. Fear of missing out (FOMO) or panic selling can lead to impulsive actions, resulting in poor trading outcomes. Maintaining discipline and following a well-defined trading plan is essential.
Pullback trading is a valuable strategy for recognizing temporary price movements within a broader trend. By understanding the characteristics and implications of pullbacks, traders can identify opportunities and enhance their trading strategies effectively.
Incorporating pullback strategies can significantly improve a trader’s ability to navigate market trends. While pullbacks present opportunities, it is essential to remain vigilant about potential limitations and maintain a disciplined approach for successful trading outcomes.