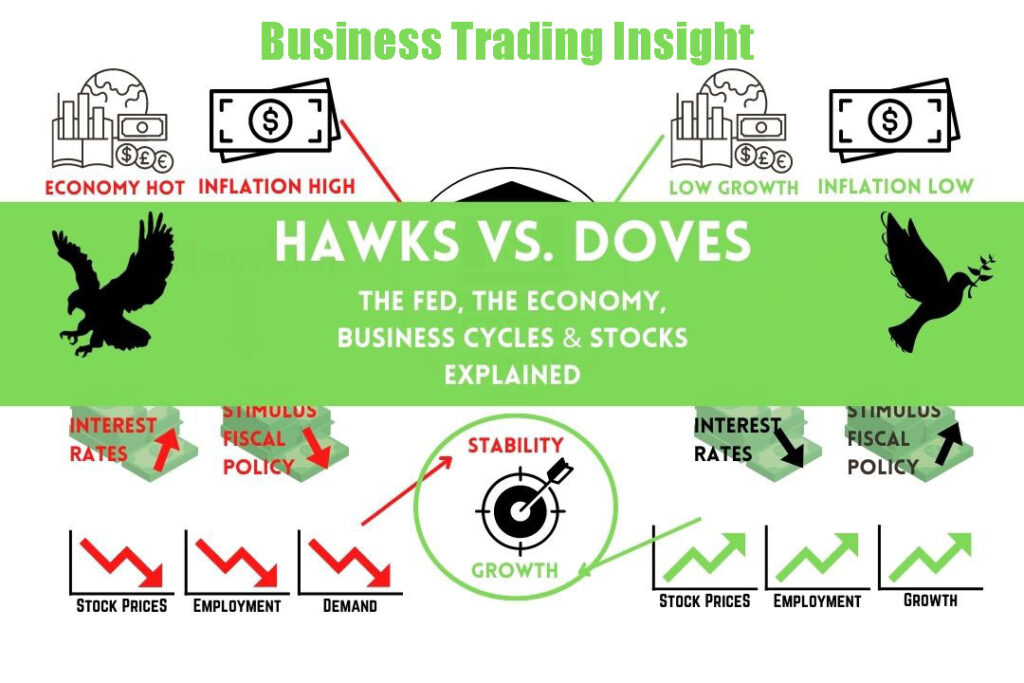
In economic and monetary policy discussions, the terms «hawks» and «doves» are crucial for understanding the differing approaches that policymakers take towards managing the economy. Hawks are typically associated with a preference for tighter monetary policies, which often includes raising interest rates to control inflation. Doves, on the other hand, advocate for looser monetary policies, favoring lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth. This dichotomy plays a significant role in shaping economic strategies and policies that influence everything from inflation rates to employment levels.
Understanding these terms is vital for investors and policymakers alike. Recognizing whether central bank officials lean hawkish or dovish can help anticipate changes in monetary policy, which directly affect investment decisions, market movements, and overall economic stability.
What Is an Inflation Hawk?
An inflation hawk is an individual or policymaker who prioritizes controlling inflation above other economic concerns. The term emerged during the late 20th century, particularly in the context of rising inflation rates that many economies faced. Inflation hawks advocate for policies that restrict the money supply, often supporting higher interest rates to curb inflationary pressures.
Historically, figures such as Paul Volcker, who served as Chairman of the Federal Reserve in the late 1970s and early 1980s, epitomize the inflation hawk mentality. Volcker’s decision to increase interest rates significantly to combat soaring inflation is often cited as a defining moment in U.S. monetary policy history. His actions, while controversial at the time, are credited with bringing inflation under control and stabilizing the economy.
Characteristics of Inflation Hawks
Inflation hawks exhibit several distinct characteristics that define their approach to monetary policy:
- Preference for Higher Interest Rates: Inflation hawks believe that increasing interest rates can help control inflation. By making borrowing more expensive, they aim to reduce consumer spending and business investments, thereby cooling off an overheating economy.
- Focus on Controlling Inflation: Their primary concern is often to keep inflation within a targeted range, as excessive inflation can erode purchasing power and destabilize the economy.
- Belief in Long-Term Benefits: Many inflation hawks are convinced that tight monetary policy, although potentially painful in the short term, leads to greater long-term economic stability and growth. They argue that a strong commitment to controlling inflation enhances the credibility of central banks.
The Role of Inflation Hawks in Monetary Policy
Inflation hawks play a significant role in shaping central bank decisions. Their influence can be felt through:
- Central Bank Decisions: Hawkish members often advocate for higher interest rates during monetary policy meetings. Their arguments are based on the premise that current inflation levels pose a risk to the economy’s long-term health.
- Interaction with Other Policymakers: Inflation hawks frequently engage with their dovish counterparts, creating a dynamic tension within monetary policy discussions. This interplay can lead to compromises that shape the central bank’s overall strategy.
- Impact on Economic Growth and Employment Rates: While hawkish policies aim to control inflation, they can also lead to reduced economic growth and increased unemployment in the short term. Inflation hawks must balance the immediate economic impacts of their policies with the long-term goals of stability and growth.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Hawkish Policies
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|
| Potential for Long-Term Economic Stability: Controlling inflation can create a stable environment for investment and growth. | Risk of Stifling Economic Growth: Higher interest rates may deter borrowing and spending, slowing growth. |
| Prevention of Runaway Inflation: Tight monetary policy safeguards against hyperinflation, protecting the economy. | Higher Unemployment Rates in the Short Term: Increased borrowing costs can lead businesses to slow expansion, raising unemployment. |
| Increased Credibility of Central Banks: Commitment to fighting inflation enhances central banks’ reputations and effectiveness. | Possible Negative Impacts on Consumer Spending and Investment: Tighter policies can reduce consumer confidence, leading to lower spending and decreased investment. |
The Dovish Perspective
In contrast to hawks, dovish policymakers advocate for lower interest rates and more accommodative monetary policies. They prioritize economic growth and job creation over immediate inflation concerns. This approach can be particularly relevant during periods of economic downturn, where the priority is often to stimulate demand and foster recovery.
Doves argue that a flexible monetary policy can help support employment and economic activity, even if it means tolerating slightly higher inflation levels. They contend that lower interest rates can encourage borrowing, spending, and investment, which are essential for driving economic growth.
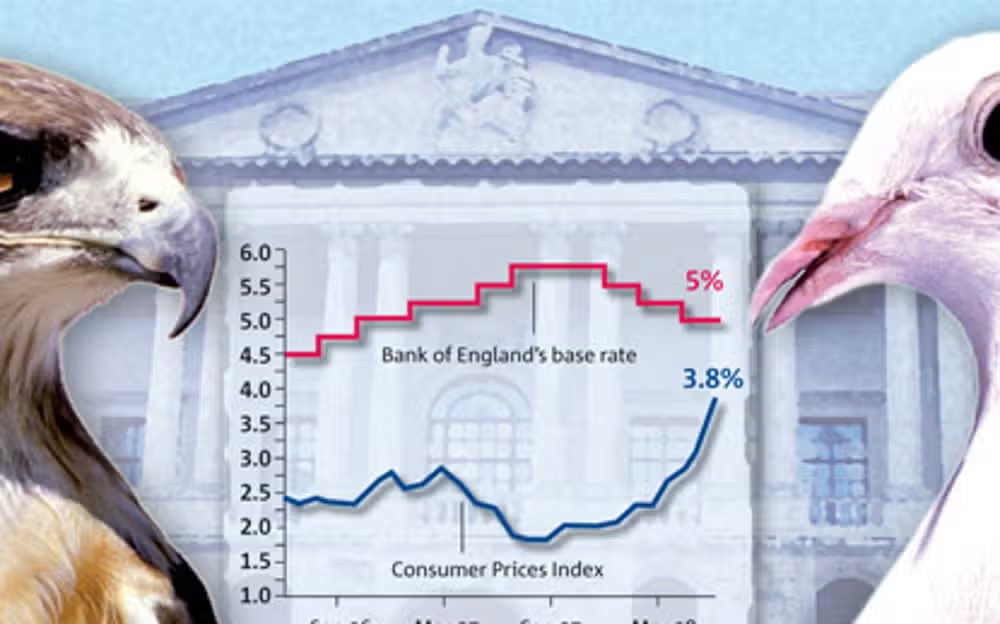
Notable Doves in History
Several notable figures in economic history have taken a dovish stance, advocating for policies that prioritize growth:
- Ben Bernanke: As Chairman of the Federal Reserve during the Great Recession, Bernanke implemented policies aimed at stimulating the economy, including quantitative easing.
- Janet Yellen: The first woman to lead the Federal Reserve, Yellen has been known for her dovish approach, focusing on maximum employment and stable prices.
Navigating the Economic Landscape
Understanding the interplay between hawkish and dovish perspectives is crucial for navigating the economic landscape. Investors must be attuned to shifts in monetary policy, as these changes can influence market trends, asset prices, and overall economic health.
Here are some strategies for investors to consider:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of central bank announcements and policy changes, as these can have immediate impacts on financial markets.
- Diversify Investments: A well-diversified portfolio can mitigate risks associated with hawkish or dovish shifts in monetary policy.
- Analyze Economic Indicators: Monitor key economic indicators such as inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth to anticipate policy changes.
The concepts of hawkish and dovish monetary policies are essential for understanding the complex dynamics of economic management. Inflation hawks play a critical role in shaping monetary policy, emphasizing the importance of controlling inflation for long-term stability. While their approach can lead to short-term challenges, the potential benefits of a stable economic environment are significant.
On the other hand, dovish policymakers highlight the importance of stimulating growth and job creation, advocating for flexibility in monetary policy. The ongoing debate between these two perspectives shapes the economic landscape and impacts decisions made by investors, policymakers, and consumers alike.
As the economy continues to evolve, the balance between hawkish and dovish strategies will remain a pivotal consideration for achieving sustainable economic growth and stability.