Digital options, or binary options, are a popular financial instrument used by traders to speculate on the price movements of assets like stocks, forex, and commodities. These options have gained significant attention due to their simplicity and the potential for high returns within a short time frame. Traders can profit by predicting whether the price of an asset will rise or fall within a specified time period.
Purpose:
This guide will provide a thorough understanding of digital options, how they work, and the strategies that traders commonly use. We’ll also explore the risks involved in trading these options, how to manage them effectively, and how you can get started safely, even as a beginner.
What Are Digital Options?
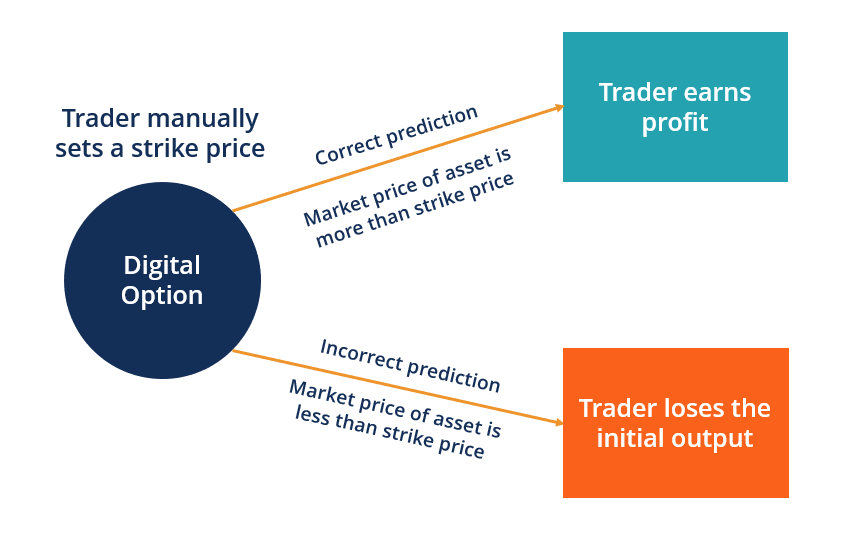
Digital options are financial instruments that allow traders to speculate on the price movement of an asset within a specified time frame. Traders must predict whether the price of the asset will go up or down at the time of expiration. If their prediction is correct, they receive a fixed payout. If wrong, they lose the amount they invested.
How They Differ from Traditional Options:
Unlike traditional options (such as call/put options), digital options offer a binary outcome. Traditional options provide payouts that depend on how far the price moves beyond the strike price, while digital options either result in a fixed payout (if the prediction is correct) or a complete loss (if the prediction is incorrect).
Why Digital Options Are Popular:
Digital options are especially attractive to beginner traders because they are simple to understand and don’t require complex strategies. The ability to make predictions about price movements in a short time frame (sometimes as little as 60 seconds) appeals to traders looking for quick returns.
How Digital Options Work: A Step-by-Step Guide
Basic Mechanics:
When trading digital options, a trader makes a prediction about whether the price of an asset will rise or fall within a specific time frame. This time frame could range from a few seconds to several hours.
Example:
Suppose you’re trading the EUR/USD currency pair. The current price is 1.1000, and you predict that it will rise above 1.1050 before the option expires. If the price hits or exceeds 1.1050, your trade is “in the money,” and you earn a fixed payout, such as 80% of your investment. If the price stays below 1.1050, your trade ends in a loss, and you forfeit your initial stake.
Strike Price and Expiration:
The strike price is the price level that the asset must reach in order for the trade to be profitable. The expiration is the moment when the trade ends, and the price at that time determines whether you’ve made a profit or loss.
Payout Structure:
The payout for a correct prediction is fixed (usually between 70% and 90% of the initial investment), and if the prediction is incorrect, the trader loses the entire invested amount.
Practical Example:
You invest $100 in a High/Low option for EUR/USD with a 80% payout. If the price moves in your favor, you earn $80. If the prediction is wrong, you lose your $100 investment.
Overview of Popular Types of Digital Options
High/Low Options:
This is the most common type of digital option, where the trader predicts whether the asset’s price will be higher or lower than the current price at the time of expiration.
Example: If EUR/USD is at 1.1000 and you predict it will rise to 1.1050 or higher by expiration, you purchase a «High» option. If it rises above 1.1050, you win a fixed payout.
One Touch/No Touch Options:
These options allow traders to predict whether the price will touch (or avoid) a certain level before expiration.
Example: You buy a One Touch option with a target price of 1.1100 for EUR/USD, and predict that the price will touch 1.1100 or higher. If it does, you win the fixed payout.
Range Options:
Traders predict whether the asset’s price will remain within a specific range at expiration.
Example: You predict that EUR/USD will stay between 1.1000 and 1.1050 during the trading period. If the price stays within that range, you win the payout.
Advantages of Trading Digital Options
Simplicity:
Digital options are straightforward, making them ideal for beginners. The basic concept involves predicting whether an asset’s price will go up or down, which is easy to grasp.
Fixed Risk and Reward:
One of the most attractive features of digital options is that the risk and reward are fixed. You know in advance how much you stand to gain or lose from each trade, making it easier to manage your capital.
Low Capital Requirements:
Compared to traditional options, digital options typically require smaller investments, making them accessible for retail traders who may not have large amounts of capital.
Short-Term Trading:
Some digital options expire in as little as 60 seconds, allowing for rapid, short-term trading opportunities.
Main Risks in Digital Options Trading
Risk of Total Loss:
The most significant risk with digital options is that you can lose 100% of your investment if the market moves against your prediction. Unlike other instruments, there is no partial payout.
Example: If you invest $100 in a High/Low option and your prediction is wrong, you lose the entire $100. There’s no way to recover part of your investment as you would with traditional options.
Market Volatility:
Sudden price movements or news events can drastically impact the outcome of your trade. High volatility can make it difficult to predict price direction accurately.
Tip: If you’re a beginner, avoid trading during times of high market uncertainty, such as during major economic announcements (e.g., interest rate decisions or employment reports).
Broker Risk:
It’s essential to choose a reliable and regulated broker, as some platforms may not be trustworthy, potentially leading to fraud or manipulation.
Tip: Before selecting a broker, ensure that they are regulated by reputable authorities like the CFTC (US), FCA (UK), or ESMA (EU). Always research a broker’s reputation and read reviews before depositing funds.
Example of a Mistake: Many beginners fail to check a broker’s regulatory status and end up trading with unregulated platforms, exposing themselves to potential scams. Always verify the platform’s legitimacy first.
Risk Management Strategies for Digital Options
1. Risk Only a Small Percentage of Your Capital:
To minimize the risk of total loss, never risk more than 2-3% of your total capital on a single trade. This way, a string of losing trades won’t significantly impact your account balance.
Example:
If your trading capital is $1,000, risk no more than $20 per trade. This helps protect you from large losses while you gain experience.
2. Diversify Your Trades:
Avoid placing all your trades in one asset or market. Diversification reduces the overall risk by spreading it across different opportunities.
3. Use Demo Accounts:
Demo accounts are invaluable tools for beginners. They allow you to practice trading without risking real money, helping you learn how to manage your trades and test strategies in real-market conditions.
Tip:
Use demo accounts on reputable platforms like IQ Option or Binary.com to practice risk management and experiment with different strategies before committing real capital.

Legal Considerations and Regulation
Global Regulatory Landscape:
Digital options are regulated differently across the world. In the EU, they are governed by ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority), while in the US, most retail trading of digital options is restricted.
Example:
As of 2024, ESMA has introduced stricter rules for brokers offering digital options in Europe, including mandatory limits on the size of bets to protect traders from significant losses.
Choosing a Regulated Broker:
When selecting a broker, ensure that they are licensed by a reputable regulatory authority. For example, in the UK, look for brokers that are registered with the FCA (Financial Conduct Authority).
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points:
Digital options are an accessible and straightforward way to trade financial markets. However, they come with risks, especially the potential for losing your entire investment. Understanding how these options work, implementing solid risk management strategies, and choosing a regulated broker are key to successful trading.
Final Thoughts:
While digital options can offer significant returns, they require careful research, strategy, and discipline. Beginners should start with a demo account to learn the ropes and avoid common mistakes.
Recommendation:
Start by practicing with a demo account, and always trade cautiously. As you gain more experience, you can refine your strategies and start trading with real money. Remember, the key to success is managing your risk and selecting a reputable broker.
FAQ
What are the main differences between digital options and traditional options?
The main difference lies in the payout structure. With digital options, the trader knows the potential profit and risks upfront because the price of the asset must either exceed or not reach a specific level at expiration. In traditional options (e.g., European or American), traders can earn profits based on the difference in the asset’s price at the time of option execution, allowing for more flexible outcomes.
What is the minimum capital required to start trading digital options?
The minimum capital needed depends on the broker and platform. Typically, you can start trading with as little as $10 to $100. However, it is recommended to start with smaller amounts and gradually increase your investment as you gain more experience.
How long does a digital options trade last?
The duration of digital options trades can range from a few seconds to several days. However, the most common are short-term options, typically lasting between 1 to 30 minutes.
Can the Martingale strategy be used in digital options trading?
Yes, the Martingale strategy can be applied in digital options trading. This strategy involves doubling the stake after each losing trade in hopes of recovering losses and making a profit. However, it carries significant risks and can lead to substantial losses if the market moves against your predictions for an extended period.