The term «NFP» stands for Nonfarm Payroll, a key economic indicator in the financial markets. It reflects the total number of paid workers in the U.S. economy, excluding farm workers, government employees, and a few other job classifications. Understanding the NFP is essential for traders and investors as it provides insights into the health of the labor market and the overall economy.
Definition of NFP
The Nonfarm Payroll report is released monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). It details the number of jobs added or lost in the economy, providing a snapshot of employment trends. The report includes various sectors, helping to gauge the performance of the economy outside of the agricultural sector.
Importance in the Financial Market
The NFP report is crucial for financial markets because it influences monetary policy and market sentiment. A strong NFP number can lead to expectations of interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve, while a weak report may prompt fears of economic slowdown. Thus, the NFP serves as a barometer for economic conditions, affecting stock prices, currency values, and bond yields.
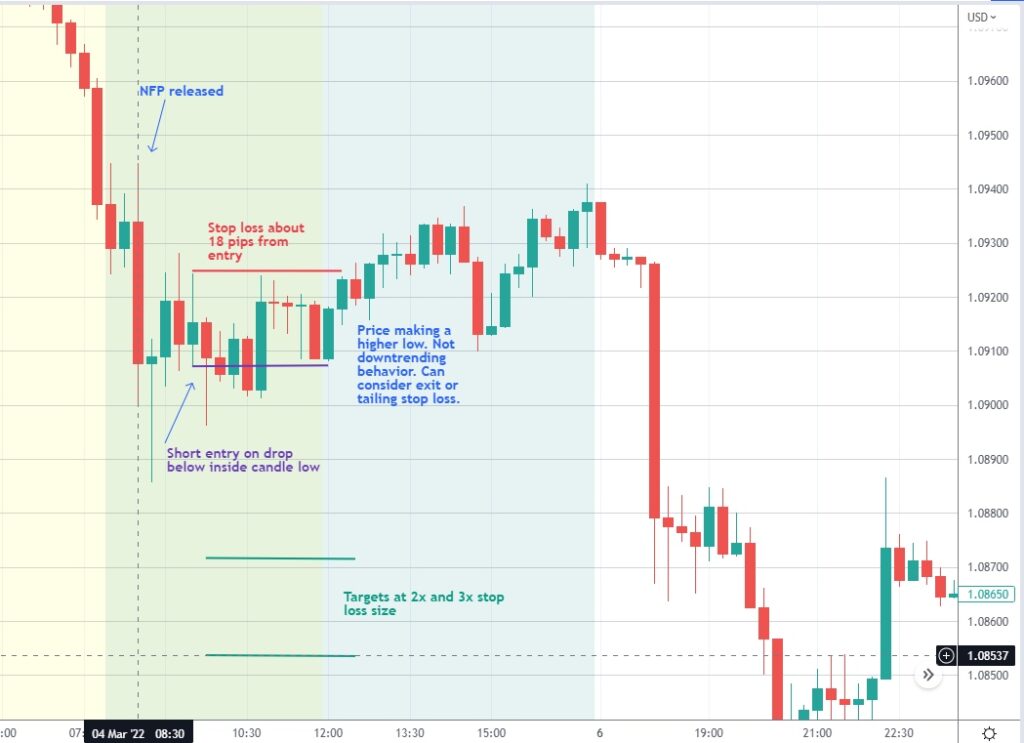
About the Nonfarm Payroll Report
Overview of the Report
The Nonfarm Payroll report is part of the broader Employment Situation report, released on the first Friday of every month. It includes key employment metrics, such as the unemployment rate, average hourly earnings, and the labor force participation rate. This data is instrumental in shaping economic forecasts and investment strategies.
What It Measures (Employment, Wages, etc.)
The NFP report measures various employment-related aspects:
- Total Nonfarm Employment: The change in the number of jobs from the previous month.
- Unemployment Rate: The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking work.
- Average Hourly Earnings: Changes in wages that provide insights into consumer spending and inflation.
Frequency and Timing of Release
The report is released monthly, specifically on the first Friday after the end of the month. This regularity allows investors and analysts to adjust their strategies based on the most current data available.
Analyzing the Nonfarm Report Numbers
Analyzing the Nonfarm Payroll report is essential for traders looking to capitalize on market movements.
How to Interpret the Data
Interpreting NFP data involves assessing the numbers in relation to expectations and historical trends.
Higher Numbers
- Implications for the Economy: A higher-than-expected NFP number typically signals a robust economy. Increased employment suggests higher consumer spending, which can drive economic growth.
- Potential Market Reactions: Strong NFP numbers often lead to bullish market sentiments, increasing stock prices and potentially prompting the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates.
Lower Numbers
- Economic Concerns and Consequences: A disappointing NFP report may indicate economic weakness, raising concerns about job growth and consumer confidence.
- Market Sentiment: Such outcomes can lead to bearish reactions in the stock market, with investors seeking safe-haven assets.
Expected Numbers
- Importance of Forecasts: Analysts typically publish forecasts for NFP figures. Meeting these expectations can stabilize market reactions, while deviations can cause volatility.
- Comparing Actual Results to Expectations: Traders often use the difference between expected and actual NFP numbers to inform their trading decisions.
Trading on News Releases
Trading based on NFP data requires careful timing and strategy.
The Significance of Timing in Trading
The NFP report is released at 8:30 AM EST, and the minutes following the announcement are often characterized by heightened volatility. Traders must be prepared for rapid price movements, making timely decisions crucial.
Strategies for Reacting to NFP Announcements
- Pre-release Positioning: Some traders position themselves before the release based on predictions and market sentiment.
- Post-release Reaction: Others wait for the report to be released, assessing immediate market reactions before entering trades.
What Is the NFP Trading Strategy?
The NFP trading strategy revolves around capitalizing on the volatility surrounding the report’s release.
Explanation of the Strategy
The strategy often involves entering trades immediately after the NFP numbers are released. Traders look for price patterns and indicators to guide their decisions.
Key Considerations for Traders
- Market Conditions: Overall market sentiment leading up to the report can influence reactions.
- Economic Indicators: Other economic data releases around the same time can affect the interpretation of NFP numbers.
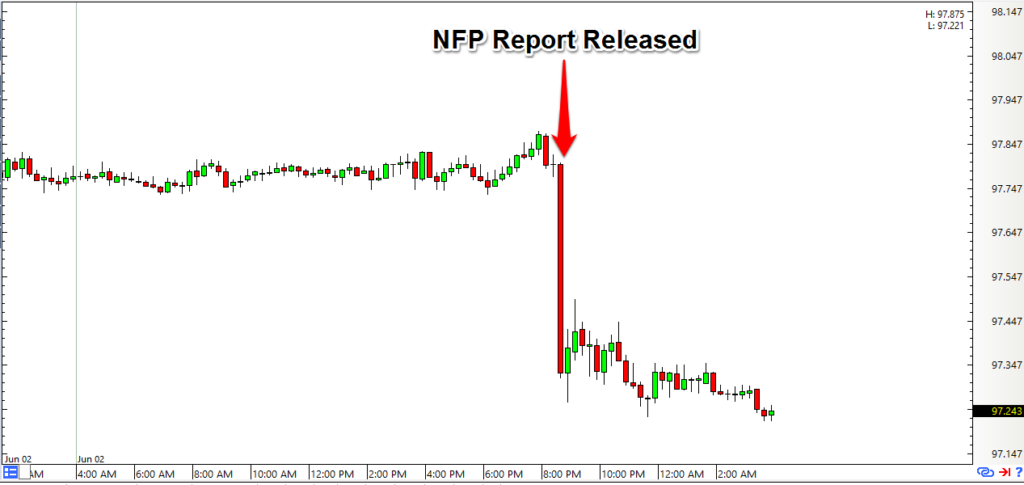
The Rules
Implementing an effective NFP trading strategy requires discipline and adherence to specific guidelines.
Guidelines for Implementing the Strategy
- Set Entry and Exit Points: Establish clear criteria for entering and exiting trades based on market conditions and price movements.
- Use Stop Loss Orders: Protect against unexpected market reversals by placing stop loss orders.
Risk Management Tips
- Limit Position Size: To mitigate risk, limit the size of your positions relative to your overall trading capital.
- Diversify Trades: Avoid putting all your capital into one trade; diversification can help spread risk.
Example of Trading the NFP Report
A practical example can illustrate the NFP trading strategy in action.
A Hypothetical Trading Scenario
Assume that the consensus forecast for the NFP report is a gain of 200,000 jobs. Upon release, the actual number comes in at 250,000. Traders might react quickly, buying into the market, expecting continued bullish momentum.
Analysis of Potential Outcomes
If the market rises sharply following the report, traders who entered early can secure profits. Conversely, if market sentiment shifts quickly due to geopolitical events or other economic indicators, traders might face losses. Analyzing these outcomes helps refine trading strategies for future reports.
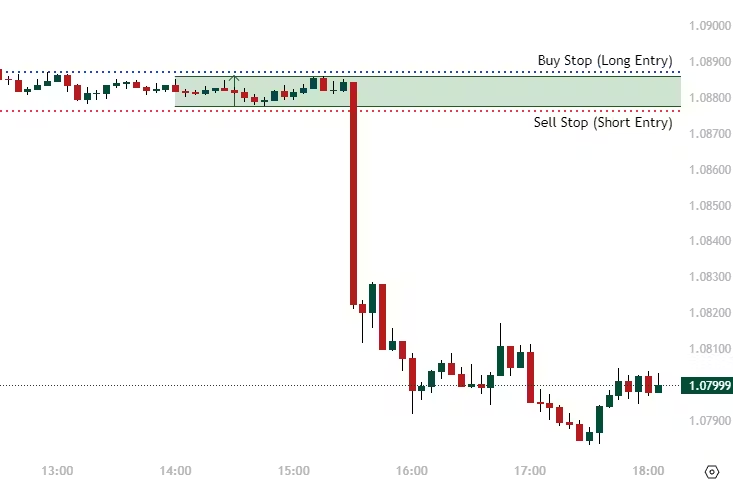
Strategy Pitfalls
While trading the NFP report can be lucrative, several pitfalls can undermine success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overleveraging: Using excessive leverage can amplify losses.
- Ignoring Market Sentiment: Disregarding the broader market context can lead to misguided trades.
Tips for Successful Trading
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of economic news and trends that could impact market movements.
- Practice Patience: Sometimes waiting for the market to settle after the initial volatility can lead to more informed trading decisions.
In summary, the Nonfarm Payroll report serves as a critical indicator of economic health and market sentiment. By understanding its implications and employing effective trading strategies, investors can navigate the complexities of the stock market with greater confidence.